How to operate a drone introduces the exciting world of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), offering a comprehensive guide to mastering this increasingly popular technology. From pre-flight checks and safety protocols to advanced flight techniques and stunning aerial photography, this guide provides a step-by-step approach for both beginners and those seeking to refine their skills. We’ll cover essential controls, navigation strategies, legal considerations, and much more, ensuring you can fly confidently and responsibly.
This exploration delves into the intricacies of drone operation, covering everything from understanding basic controls and flight modes to mastering advanced techniques like stable flight in challenging weather conditions and capturing breathtaking aerial footage. We’ll also discuss the legal framework surrounding drone use, ensuring you comply with all regulations and operate your drone responsibly. Whether you’re a novice or experienced pilot, this guide provides valuable insights and practical advice to enhance your drone flying experience.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting various components, checking weather conditions, and familiarizing yourself with emergency procedures. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents and damage.
Drone Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection ensures all drone systems are functioning correctly. The following table Artikels key components and their acceptable/unacceptable conditions.
| Component | Inspection Item | Acceptable Condition | Unacceptable Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Condition, Securement | No cracks or damage; firmly attached | Cracks, chips, or loose propellers |
| Battery | Charge Level, Condition | Sufficient charge for flight; no visible damage | Low charge; swelling, damage, or leaks |
| Gimbal | Movement, Stability | Smooth, stable movement in all directions | Jerky movement, stiffness, or unusual noises |
| Camera | Lens, Functionality | Clean lens; proper image display | Dirty or scratched lens; malfunctioning camera |
| Airframe | Structural Integrity | No cracks, bends, or damage | Any signs of damage to the drone body |
| Radio System | Signal Strength, Connection | Strong signal; solid connection with the controller | Weak signal; intermittent connection |
Weather Considerations
Adverse weather conditions significantly impact drone flight safety. High winds, heavy rain, snow, or fog can reduce visibility, affect drone stability, and increase the risk of accidents. Always check the forecast before flying.
Examples of unsafe weather conditions include wind speeds exceeding the drone’s specified limits (often around 20 mph/32 km/h), heavy precipitation reducing visibility, and thunderstorms presenting a significant electrical hazard. Fog and low cloud cover can also create visibility issues.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Using a checklist ensures all safety measures are addressed before each flight.
- Inspect all drone components (propellers, battery, gimbal, camera, airframe).
- Check battery charge level.
- Verify GPS signal strength.
- Review weather conditions (wind speed, precipitation, visibility).
- Confirm airspace regulations and identify potential no-fly zones.
- Test controller responsiveness.
- Perform a pre-flight calibration (if necessary).
- Have a designated observer present.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is vital. Loss of signal or drone malfunction requires immediate action.
- Loss of Signal: Most drones have a “Return-to-Home” (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If RTH fails, attempt to manually guide the drone back, prioritizing a safe landing area.
- Drone Malfunction: If the drone exhibits unusual behavior (uncontrolled movement, erratic flight), immediately attempt to land the drone in a safe location. If this is not possible, prioritize the safety of people and property.
Understanding Drone Controls and Flight Modes

Understanding drone controls and flight modes is fundamental to safe and effective operation. Different flight modes cater to various skill levels, allowing for controlled progression.
Drone Control Sticks
Standard drone controllers typically have two control sticks, each controlling different aspects of the drone’s movement.
- Left Stick: Controls the drone’s altitude and yaw (rotation). Pushing the stick up increases altitude, pushing it down decreases altitude. Moving the stick left or right rotates the drone.
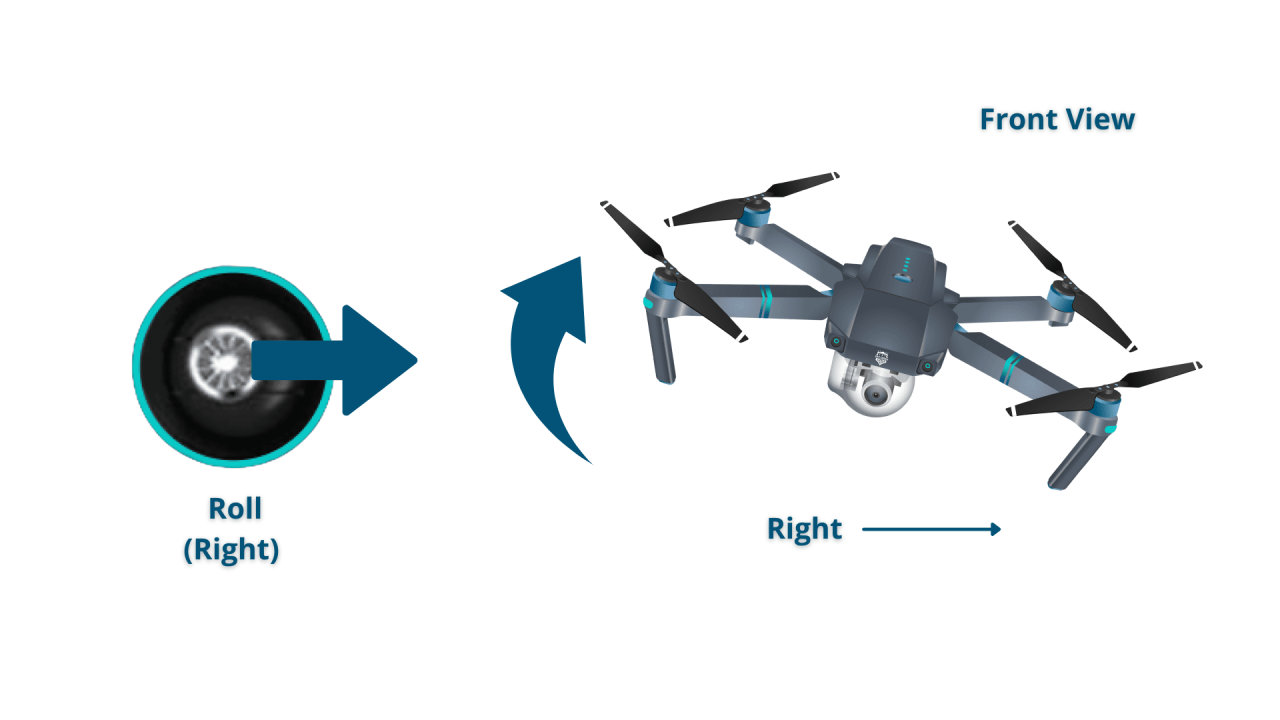
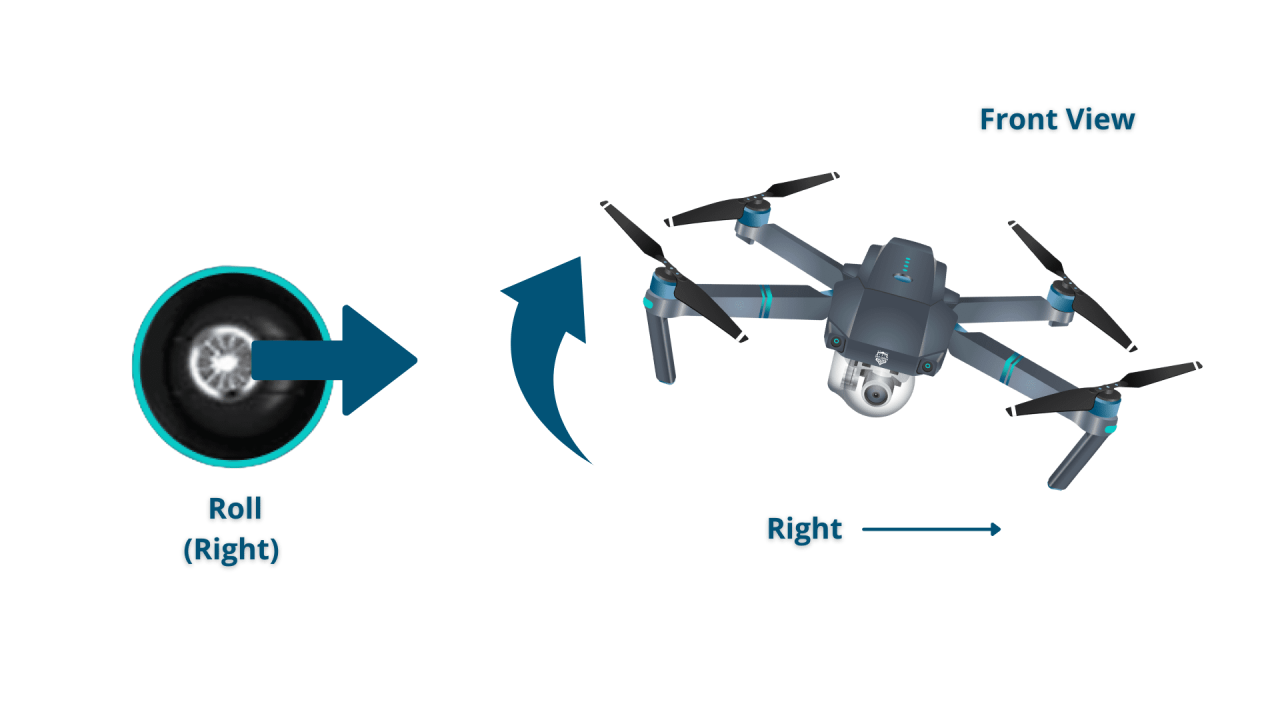
- Right Stick: Controls the drone’s pitch (forward/backward movement) and roll (left/right movement). Pushing the stick forward moves the drone forward, pushing it back moves it backward. Pushing it left or right moves the drone sideways.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability.
- Beginner Mode: Limits the drone’s speed and responsiveness, ideal for learning.
- Sport Mode: Allows for faster speeds and more agile maneuvers, suitable for experienced pilots.
- Manual Mode: Provides full control over the drone’s movements, requiring significant skill and experience.
Safe Takeoff and Landing
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are critical for preventing accidents.
- Ensure the area is clear of obstacles.
- Calibrate the drone’s compass and GPS.
- Slowly lift the drone vertically until it reaches a stable hover.
- For landing, slowly lower the drone vertically until it touches down gently.
Adjusting Drone Settings

Adjusting drone settings optimizes safety and performance. These settings can often be modified through the drone’s mobile application.
- Altitude Limits: Set maximum and minimum altitude limits to prevent accidental high-altitude flights or ground collisions.
- Return-to-Home (RTH) Settings: Ensure the RTH function is properly configured and the home point is accurately set.
- Emergency Stop: Familiarize yourself with the emergency stop procedure for your specific drone model.
Navigation and Flight Techniques
Effective navigation and flight techniques enhance safety and enable efficient drone operation. Understanding GPS functionality and adapting to different flight conditions is essential.
GPS Functionality
GPS (Global Positioning System) is crucial for drone navigation. It allows the drone to determine its location, maintain position, and return to its starting point. The drone receives signals from multiple GPS satellites to calculate its precise coordinates. A diagram would show a drone receiving signals from multiple satellites, with the intersection of those signals pinpointing the drone’s location.
Flying in Windy Conditions
Wind can significantly impact drone stability. Maintaining stable flight requires specific techniques.
- Increase your control inputs to compensate for wind gusts.
- Fly into the wind for easier control during takeoff and landing.
- Avoid flying in extremely windy conditions.
Tips for Smooth and Efficient Flight
Smooth and efficient drone operation requires practice and attention to detail.
- Maintain a consistent speed and altitude.
- Plan your flight path beforehand.
- Use smooth, controlled movements to avoid jerky flight.
- Practice regularly to improve your skills.
Flying in Confined Spaces
Flying drones in confined spaces presents unique challenges, demanding precise control and obstacle awareness.
- Use lower speeds and more deliberate movements.
- Carefully assess the environment for potential obstacles.
- Practice flying in similar environments before attempting complex maneuvers.
Drone Photography and Videography Basics
Capturing high-quality aerial images and videos requires understanding camera settings, composition techniques, and flight planning. Utilizing drone features enhances creativity and image quality.
Camera Settings, How to operate a drone
Adjusting camera settings is crucial for achieving optimal image quality.
- ISO: Controls the sensitivity to light. Lower ISO values produce cleaner images, but require more light. Higher ISO values are useful in low-light conditions but can introduce noise.
- Shutter Speed: Determines how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower shutter speeds create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the camera lens. A wider aperture (lower f-number) creates a shallow depth of field, blurring the background. A narrower aperture (higher f-number) increases depth of field, keeping both foreground and background in focus.
Composition Guide
Effective composition enhances the visual appeal of aerial shots. The rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry are key compositional elements.
A good composition might showcase a subject placed along a leading line that draws the viewer’s eye, using the rule of thirds to create visual balance. A poor composition might center the subject, creating a static and less engaging image.
Flight Planning
Planning your drone flight is crucial for achieving your photography or videography goals. Consider lighting, composition, and the desired shot before takeoff.
- Determine the best time of day for lighting.
- Identify ideal locations and angles for your shots.
- Plan your flight path to capture the desired footage efficiently.
Utilizing Drone Features
Drone features like gimbals and zoom capabilities significantly enhance image quality and creative possibilities.
- Gimbal: Stabilizes the camera, resulting in smoother footage, even during flight.
- Zoom: Allows you to get closer to your subject without physically moving the drone.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly involves adhering to all relevant laws and regulations. Understanding airspace restrictions and obtaining necessary permits is crucial to avoid penalties and ensure safe operation.
Drone Regulations
Drone regulations vary by region. It’s essential to research and understand the specific laws in your area. The following is a general example and may not reflect your local regulations.
| Regulation | Description | Penalties for Violation | Relevant Websites/Resources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drone Registration | Registering your drone with the relevant aviation authority. | Fines, impoundment of drone | [Insert relevant website for your region] |
| Airspace Restrictions | Restrictions on flying near airports, sensitive areas, or crowded spaces. | Fines, potential legal action | [Insert relevant website for your region] |
| Flight Limitations | Restrictions on flight altitude, distance, and operational times. | Fines, suspension of operating privileges | [Insert relevant website for your region] |
| Privacy Regulations | Restrictions on recording individuals without their consent. | Fines, legal action | [Insert relevant website for your region] |
Drone Registration and Permits
Registering your drone and obtaining necessary permits are often required before operation. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties.
Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones
Numerous airspace restrictions exist, including areas around airports, military bases, and other sensitive locations. These areas are designated as no-fly zones, and entering them without authorization is illegal.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone. Safe and responsible drone piloting is crucial for both personal safety and the enjoyment of this exciting technology.
Responsible Drone Operation
Responsible drone operation includes respecting privacy, avoiding hazardous situations, and adhering to all applicable laws and regulations. This contributes to a safe and enjoyable drone flying experience for everyone.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of technical skill, responsible awareness, and a keen eye for detail. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of pre-flight procedures, flight controls, navigation techniques, and legal compliance, equipping you with the knowledge to safely and effectively operate your drone. Remember that continuous practice and adherence to safety guidelines are crucial for improving your skills and ensuring responsible drone use.
Embrace the possibilities of aerial exploration, but always prioritize safety and ethical considerations. Happy flying!
Common Queries: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with features like GPS stabilization and automated return-to-home functions are ideal for beginners. Research models known for their ease of use and robust safety features.
How long does it take to become proficient at flying a drone?
Proficiency varies, but consistent practice and familiarization with your drone’s features will lead to improved skills over time. Expect a learning curve, and prioritize safe practice sessions.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. A crucial aspect is learning about pre-flight checks and navigation; for comprehensive guidance, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone effectively. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone usage, ultimately enhancing your aerial experience.
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If the signal is lost, the drone will attempt to return to its takeoff point. Consult your drone’s manual for specific RTH procedures.
How do I ensure my drone footage is legally compliant?
Always check local and national regulations regarding drone operation, particularly concerning privacy and airspace restrictions. Obtain necessary permits and avoid flying in restricted zones.